About clustering
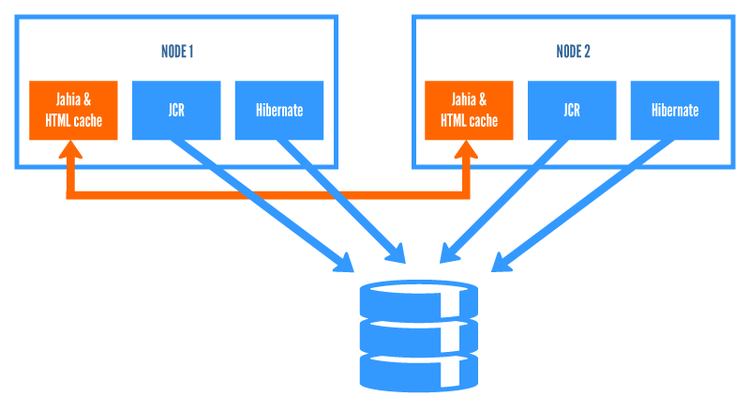
Deploying Jahia in a cluster is an effective way of distributing CPU and memory load to handle larger traffic sites. The image below illustrates a typical Jahia cluster installation. Jahia nodes communicate with each other through cache and database layers, but also access shared resources: a shared file system and the database. The file system is used for the binary content if the server is configured to store it there, or in the database if the default configuration is used. The database stores everything else. It is therefore very important to have a high-performance database installation, as Jahia will depend on it to scale. Jahia can also differentiate nodes in a cluster setup in order to offer more specialized processing. We will review here quickly the different node types.
Processing node
The processing node executes long-running tasks, such as workflow validation operations, copy and pasting, content import and indexing, as background tasks. This enables other nodes to process content browsing and editing requests. This node is designed to be fault-tolerant. If the node fails during processing, it can simply be restarted and it will resume operations where it left off. Note that only one processing node is permitted.
Other nodes (browsing & authoring)
Other nodes are not typically not specialized: they can serve for browsing (serving content to visitors) and authoring (supporting authoring actions of content authors). In some specific setup, for instance with a lot of traffic and a high number of User Generated Content (User Generated Content) it might be required to split the authoring and browsing nodes. In case of doubt on the sizing, our support or professional services teams will be happy to help, even though sizing will depend a lot on your implementations.
More resources on performance
As Jahia constantly strives to improve on performance, make sure to check our website for additional resources on performance, as well as our Configuration and Fine Tuning documentation and Setting up a high availability environment documentation that contain best practices of deployment and configuration to properly setup Jahia for high loads.