Specifying internationalization settings
Sites languages
When creating a site you will be asked to associate it with at least one language, this will define the language you can access on your site. After the creation of the site you can go to your site administration panel in the administration center, to add/remove languages from your site define which ones are mandatory and which one is the default language.
The structure of the site is the same in all languages - only internationalized fields will use different content. Any content created in one language needs to be translated to be displayed in another language. Note that deleting a content will delete it in all languages - there's only one content with multiple translations.
Default language
The default language will be used when accessing the site for the first time, and if the mixin language option is activated.
Mandatory language
Mandatory languages only impact the way you can publish a node in edition or the way you can see a node in live mode. This has only an impact on nodes having mandatory properties. As a reminder, a node with mandatory properties must have a value for all of them in order to be valid in the current language. Only a valid node can be published. If a mandatory property is missing, a red flag will appear in the publication status :
In addition, a node MUST have a value in each mandatory language for each of its mandatory properties to be valid in ANY language.
However, once the node is valid, each language will have its own workflow so they can be really published at a different time.
If a node is created and not translated in one mandatory language, a green flag will appear as the publication status :
In live mode, a node needs to be valid to be visible. So it MUST have a value in each mandatory language for each of its mandatory properties to allow it to be seen by users.
So if you have two mandatory languages for example (en,fr) each page you create must have a title in both languages to be published. To be seen in live, a page must have ended its workflow on each language, if the English workflow for my page is finished on Monday. And the one in French in finished on Tuesday my English page will only be visible for my end users on Tuesday when the French workflow is over even if my page in English exist in my live repository since Monday.
Mix language
Mix language allows displaying the content even if it not translated, by using the default language instead. Click on the mix language button in language administration to activate the option.
If a node has not been translated in the currently selected language, Jahia will fallback to default language to display it.
A node is considered translated as soon as one of its internationalizable properties exist in the selected language.
If a node has no internationalizable properties then it is the same one for all languages - mix language option has no effect on these nodes.
Deleting a language
Deleting a language in Jahia is a non-destructive action, this will only remove the language from the available languages in your site, this will not erase any content from your repository (as your content could be reused anywhere in this language).
So if you restore this language in the available list of language, you will retrieve your site as it was before the language deletion.
Language resolution
When a first request is done to Jahia, without specifying a path and language, Jahia tries to guess in which language the user must be redirected. It looks for the possible languages in the following order :
- User language preference
- Browser language preference
- Default language for the site
The first language available for the current site will be used.
Internationalized fields
An internationalized field will have a different value for each language.
A field can be marked as internationalized by adding the keyword internationalized, or i18n, in the CND file. Any field type can be marked as internationalized.
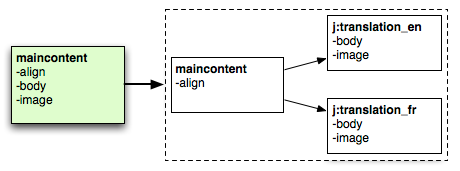
[jnt:mainContent] > jnt:content, mix:title, jmix:structuredContent, jmix:editorialContent
- body (string, richtext) i18n
- image (weakreference, picker[type='image']) i18n
- align (string,choicelist[resourceBundle]) = left indexed=no < left,right,default
In this example, body and image fields are internationalized. The text and the associated image will be different for every language.
Internationalized fields are marked with a small flag icon in the edit engines :
Note that the align field is not internationalized - but the displayed label will be different depending on the selected language. The value itself is shared between all languages - but the resourceBundle keyword tells the value is a resource bundle key.
Content model
Internationalized fields are stored in a special sub-node of the content. The subnode is named j:translation_lang and has the type jnt:translation . This type is basically unstructured and will store all internationalized properties of its parent.
Using localized and unlocalized sessions
Translation nodes are usually hidden for the user - as long as the session is opened with a locale (localized session), internationalized properties are transparently returned by getProperty() methods and other API. Translation nodes will be seen when using a non-localized session.
Opening a localized session can be done by using the following method from JCRSessionFactory :
public JCRSessionWrapper getCurrentUserSession(String workspace, Locale locale) throws RepositoryException;
Or other methods from JCRSessionFactory and JCRTemplate taking the locale as a parameter.
Note that the sessions used for rendering, available in the JSP views, are localized.
Publication
The lifecycle of the translation nodes is separate from the one their parent node - they can be published independently.